Google Ads bidding strategies are at the heart of driving cost-effective results in your campaigns. Understanding how to use bid strategies effectively can significantly impact your campaign’s success. Whether your goal is to maximize clicks, impressions, conversions, or ROAS, selecting the right bidding strategy can make or break your campaign’s success. This blog will walk you through how to use Google Ads bidding strategies effectively, explore Google Ads strategies, and help you understand how to choose the best approach for your needs.
Manual CPC allows advertisers to set individual bids for each keyword or ad group. It provides full control over costs and is especially useful for campaigns with limited budgets or highly competitive keywords.
2025 Update: Manual CPC is becoming less effective as Google prioritizes smart bidding in auctions. Consider switching to Maximize Conversions for better results.
Enhanced CPC blends manual bidding with Google’s automated tools to adjust bids based on the likelihood of a conversion. This strategy is a middle ground between manual control and automation.
2025 Update: According to recent Google Ads updates, the “Enhanced CPC” (ECPC) bid strategy is being phased out, meaning it will no longer be available for new campaigns starting in October 2024 and will be completely removed for all existing campaigns by March 2025.
Maximize Clicks is a fully automated strategy where Google adjusts bids to generate the maximum number of clicks within your budget. This is ideal for driving traffic in awareness campaigns.
2025 Update: Google’s AI is getting better at understanding user intent—consider pairing Maximize Clicks with broad match keywords + smart audiences for better targeting.
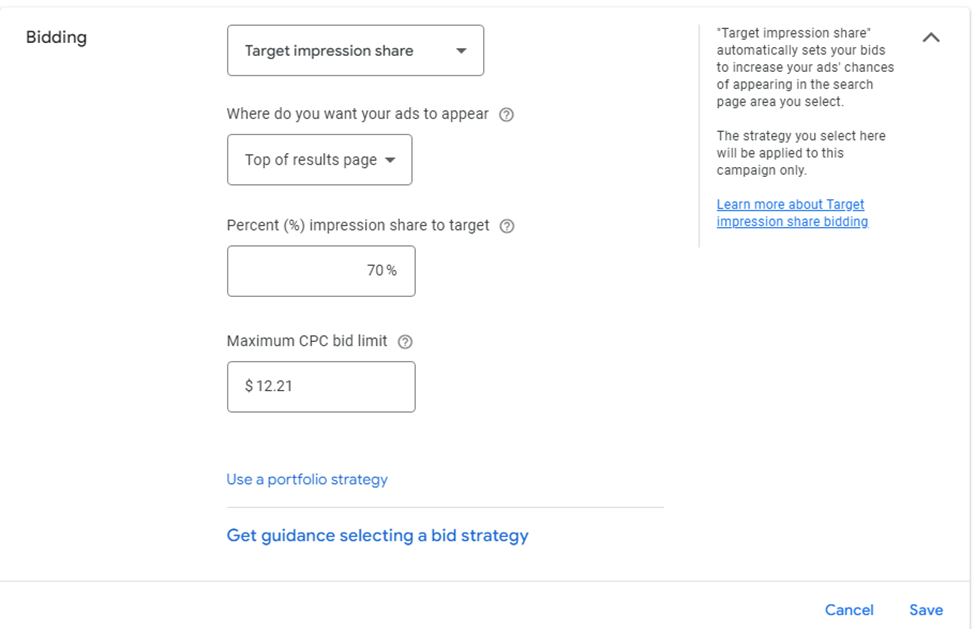
Target Impression Share ensures your ad appears in a specific position on the search results page or achieves a certain share of impressions, making it a popular choice for visibility-focused campaigns.
2025 Update: Google is moving towards Performance Max campaigns, which prioritize visibility + conversion intent, making this strategy less necessary.
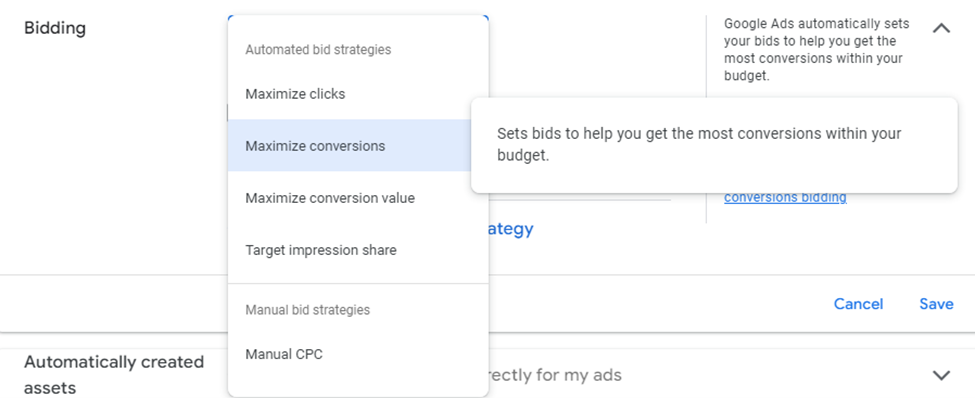
Maximize Conversions uses Google’s algorithms to optimize bids for the highest number of conversions within a specified budget. This strategy is excellent for lead generation or customer acquisition.
2025 Update: Performance Max & Smart Bidding now improve Maximize Conversions by analyzing user intent signals for better lead quality.
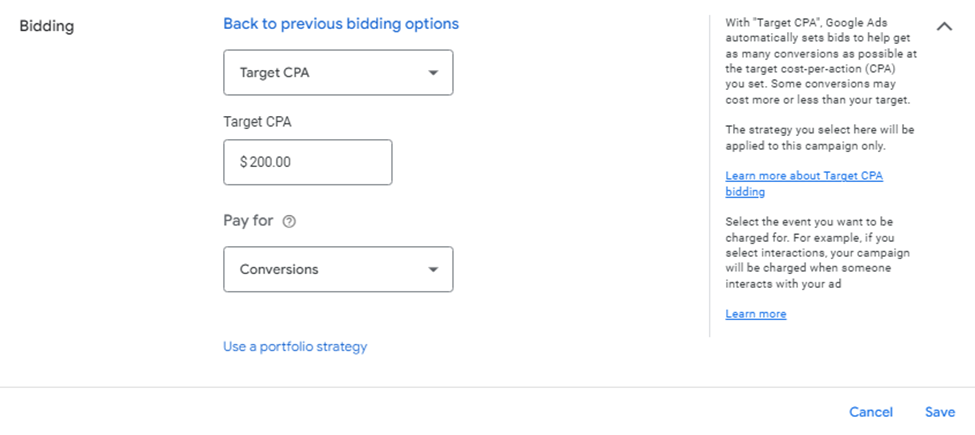
Target CPA focuses on achieving conversions at a specific cost per acquisition. It’s particularly effective for campaigns aiming to generate predictable conversion costs.
2025 Update: Google now recommends starting with Maximize Conversions before switching to Target CPA to allow AI to gather better bid insights.
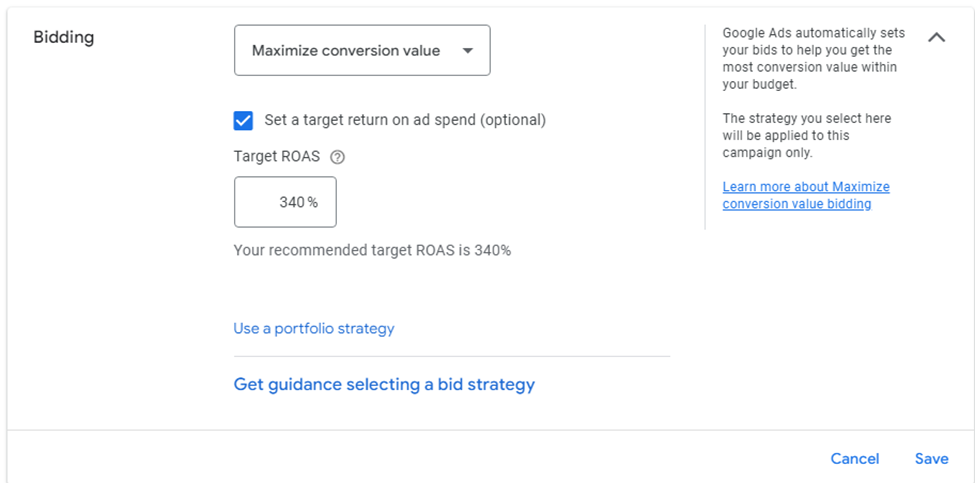
Target ROAS optimizes bids to achieve a predefined return on ad spend, making it ideal for eCommerce or revenue-driven campaigns.
2025 Update: Google has improved conversion value tracking & AI-driven optimization, making Target ROAS highly effective when combined with broad match keywords.
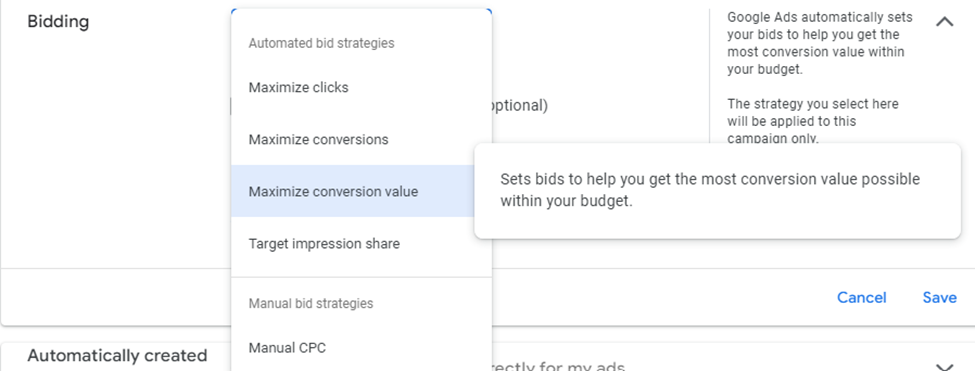
Maximize Conversion Value prioritizes high-value conversions over quantity by optimizing for total conversion value within a given budget.
2025 Update: This bid strategy now works seamlessly with Performance Max for better revenue-focused scaling.
CPM bidding charges advertisers per 1,000 impressions, making it an effective choice for increasing brand awareness and visibility.
2024 Update: CPM campaigns now integrate better with Google Display & Video 360, providing improved brand reach tracking.
CPV bidding is specific to video campaigns and charges advertisers for views or interactions, making it ideal for engaging audiences on platforms like YouTube.
| Campaign Type | Objective | Recommended Bid Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Awareness | High Impression | Target Impression Share |
| Website Traffic | Drive Clicks | Maximize Clicks |
| Lead Generation | Low CPA | Maximize Conversion with Target CPA |
| Revenue Growth | Maximize Revenue | Maximize Conversion with Target ROAS |
| Video Campaign | Increase Views | Target CPV |
| Retargeting | Re-engage Visitors | Maximize Conversion |
Selecting the right Google Ads bidding strategy is essential for achieving your campaign goals. This blog has outlined the various options, their use cases, potential pitfalls, and how to align them with your objectives and your target audience. By leveraging these Google Ads strategies effectively, you can optimize your campaigns and achieve measurable success. If you’re wondering how to choose the best bidding strategy for Google Ads, start by understanding your goals and aligning your bid strategy to meet them.
Share this blog